|
| | Blood Chemicals May
Predict Autism & Mental Retardation
There are biological markers in a newborn’s blood that may be usable to predict the risk of the child later developing autism or mental retardation, according to researchers. This remarkable discovery was announced this spring during the annual meeting of the American Academy of Neurology in San Diego.
If proven to be true, this might open the door to accelerating treatment for these disorders. The research was conducted using blood samples collected by the California Birth Defects Monitoring Program.
The CBDMP obtains and preserves blood samples from 1 in 7 babies born in California each year and uses the blood to track down causes of birth defects.
By examining the blood of babies born during the early 1980’s, the researchers were able to identify four abnormal proteins in each of the children that later had developed the severe social withdrawal found in autism, or the low I.Q found in children with mental retardation.
Since many of the causes of these disorders are currently not diagnosed for 2 to 4 years after birth, an ability to identify the infants who may have these abnormalities could lead to earlier and more appropriate treatment.
To date, the study has involved the testing of 249 individuals. These promising results will now be subjected to a validation study which will include as many as 5,000 children with autism or mental retardation, and compared to an equally large control group of healthy children.
Test Chemicals
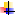 | Vasoactive intestinal peptide |
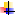 | Brain-derived neurotrophic factor |
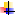 | Neurotrophin—4 |
 | Calcitonin-related gene peptide
|
Autism
Autism is a neurological disorder that affects the functioning of the brain. Ordinarily the disorder appears during a child’s toddler years and obstructs their normal development. No cure is known. Early intervention often reduces undesirable behaviors and results in improved development and educational outcomes.
The Autism disorder results in severe impairment of a person’s abilities. This often includes an inability to communicate due to poor languages skills, atypical movement and motor control, and a persistent failure to develop normal social relationships.
Autism is estimated to affect more than 400,000 people in the United States, according to the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke. It has been found in families of all ethnic, racial, and social backgrounds. The worldwide incidence of Autism has been reported to be about 1 case in every 2,500 births. The disorder is found about four times more frequently in males as in females.
The California Birth Defects Monitoring
Program
http://www.cbdmp.org
(888) 898-2229
Back to Issue - May/June 2000
Back to 

|

![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()